Arch + Repositórios do Manjaro - Monarch
Gosta das facilidades do Manjaro? Não gosta das frescuras do Manjaro com multiboot ou pendrives? Então esse artigo é pra você! Faça seu "Monarch".
[ Hits: 10.394 ]
Por: Silas Henrique em 23/09/2017 | Blog: https://silas.eng.br
Instalação do Arch
Avisos de segurança
Mudar repositórios de qualquer distro, pode causar instabilidade e bugs imprevisíveis! Caso você seja iniciante no Linux, prefira o próprio Manjaro original. Mas, se você gosta de customizar o Arch Linux e quiser mudar até aquilo que não deveria ser mudado, seja bem vindo.Instalação normal
A instalação do Arch Linux é bem diferente das distros "comuns". Ela é feita totalmente por linha de comando. Recomendo que leia o Wiki da distro em português:Ou, o artigo daqui do Viva o Linux:
Achou complicado? O Arch Anywhere pode ajudar:
Se optar por esse tipo de instalação, alguns bugs podem ocorrer como pacotes mais novos que os dos repositórios.
Instalação da interface gráfica
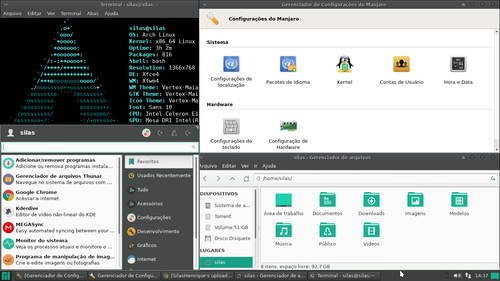
O Manjaro Linux tem como interface gráfica padrão o XFCE, mesmo tendo outras Flavors. Então, eu irei utilizar como exemplo o XFCE (não testei com outras interfaces gráficas).Após seu Arch estiver instalado, instale o XFCE e configure o painel para ficar na parte de baixo.
instale um gerenciador de pacotes gráfico, como o Octopi (a menos que você saiba o nome dos pacotes necessários).
Instale pacotes, como:
- xfce4-clipman-plugin
- xfce4-pulseaudio-plugin
- xfce4-screenshooter
- xfce4-whiskermenu-plugin
Alterando os repositórios
Finalmente a parte mas esperada, a mudança de repositórios!1. Escolha um mirror no site: http://repo.manjaro.org/
Recomendo o: https://mirror.math.princeton.edu
2. Não é possível instalar mais de 1 mirror, o que deixa os downloads um pouco lentos.
3. Faça um backup do arquivo /etc/pacman.conf.
4. Rode no terminal:
sudo thunar
5. Abra o arquivo /etc/pacman.conf com seu editor de texto preferido, previamente instalado.
6. Exclua tudo e cole:
# /etc/pacman.conf
#
# See the pacman.conf(5) manpage for option and repository directives
#
# GENERAL OPTIONS
#
[options]
# The following paths are commented out with their default values listed.
# If you wish to use different paths, uncomment and update the paths.
#RootDir = /
#DBPath = /var/lib/pacman/
#CacheDir = /var/cache/pacman/pkg/
#LogFile = /var/log/pacman.log
#GPGDir = /etc/pacman.d/gnupg/
#HookDir = /etc/pacman.d/hooks/
HoldPkg = pacman glibc
#XferCommand = /usr/bin/curl -C - -f %u > %o
#XferCommand = /usr/bin/wget --passive-ftp -c -O %o %u
#CleanMethod = KeepInstalled
#UseDelta = 0.7
Architecture = auto
# Pacman won't upgrade packages listed in IgnorePkg and members of IgnoreGroup
#IgnorePkg =
#IgnoreGroup =
#NoUpgrade =
#NoExtract =
# Misc options
#UseSyslog
#Color
#TotalDownload
CheckSpace
#VerbosePkgLists
# By default, pacman accepts packages signed by keys that its local keyring
# trusts (see pacman-key and its man page), as well as unsigned packages.
SigLevel = Required DatabaseOptional
LocalFileSigLevel = Optional
#RemoteFileSigLevel = Required
# NOTE: You must run `pacman-key --init` before first using pacman; the local
# keyring can then be populated with the keys of all official Arch Linux
# packagers with `pacman-key --populate archlinux`.
#
# REPOSITORIES
# - can be defined here or included from another file
# - pacman will search repositories in the order defined here
# - local/custom mirrors can be added here or in separate files
# - repositories listed first will take precedence when packages
# have identical names, regardless of version number
# - URLs will have $repo replaced by the name of the current repo
# - URLs will have $arch replaced by the name of the architecture
#
# Repository entries are of the format:
# [repo-name]
# Server = ServerName
# Include = IncludePath
#
# The header [repo-name] is crucial - it must be present and
# uncommented to enable the repo.
#
# The testing repositories are disabled by default. To enable, uncomment the
# repo name header and Include lines. You can add preferred servers immediately
# after the header, and they will be used before the default mirrors.
# If you want to run 32 bit applications on your x86_64 system,
# enable the multilib repositories as required here.
# An example of a custom package repository. See the pacman manpage for
# tips on creating your own repositories.
#[custom]
#SigLevel = Optional TrustAll
#Server = file:///home/custompkgs
[core]
SigLevel = Optional TrustAll
Server = https://mirror.math.princeton.edu/pub/manjaro/stable/core/x86_64/
[extra]
SigLevel = Optional TrustAll
Server = https://mirror.math.princeton.edu/pub/manjaro/stable/extra/x86_64/
[multilib]
SigLevel = Optional TrustAll
Server = https://mirror.math.princeton.edu/pub/manjaro/stable/multilib/x86_64/
[community]
SigLevel = Optional TrustAll
Server = https://mirror.math.princeton.edu/pub/manjaro/stable/community/x86_64/
7. Salve o arquivo. Caso queira usar outro repositório, é só substituir todos os https://mirror.math.princeton.edu pelo seu mirror.
Caso queira usar versões testing dos pacotes, substitua todos os "stable" por "testing".
Instalação dos programas Manjaro
1. Abra o Octopi.2. Vá na aba "arquivo" e clique em: Sincronizar base de pacotes.
3. Instale o pamac e abra-o.
4. Instale os seguintes pacotes:
- maia-console
- maia-wallpaper
- maia-xfce-icon-theme
- vertex-maia-icon-theme
- vertex-maia-themes
- xcursor-maia
- manjaro-artwork
- manjaro-icons
- manjaro-settings-manager
- manj-grub
- yaourt
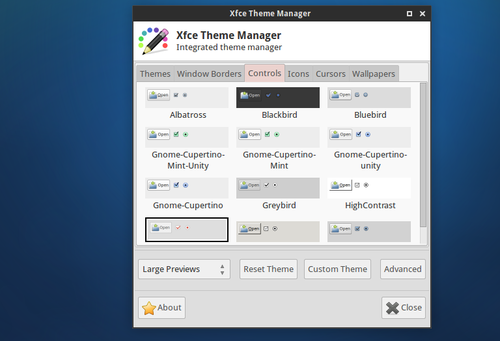
Para ajudar na customização, instale o pacote "xfce-theme-manager" pelo repositório AUR.
Toques finais
1. Configure os temas pelo "Xfce-theme-manager": 2. Adicione os itens extras no Painel.3. Mude o Papel de Parede.
Confira o resultado:
O Wine as avessas: como rodar o Linux no Windows 10
Squirrelmail em português sem gambiarra
XL - Ferramenta de gerenciamento Xen - Parte II
Monitoração com Zabbix no Debian Squeeze
Instalando o CVS no Ubuntu Linux
Instalando DRBD + Heartbeat no Debian 6
Gostei do nome Monarch. Ficou bastante criativo.
nos teus testes, como ficou a questão compatibilidade de pacotes? dependências (principalmente após a mudança dos repositórios)? e arquivos de configurações? não sou usuário do manjaro, mas acredito que existam mais arquivos de configurações diferentes do que apenas o pacman.conf.
[2] Comentário enviado por niquelnausea em 26/09/2017 - 22:26h
nos teus testes, como ficou a questão compatibilidade de pacotes? dependências (principalmente após a mudança dos repositórios)? e arquivos de configurações? não sou usuário do manjaro, mas acredito que existam mais arquivos de configurações diferentes do que apenas o pacman.conf.
Escreva o comando :
pacman -S $(pacman -Qnq)
Assim ele vai reinstalar TODOS os pacotes e corrigir qualquer incompatibilidade que você encontre ! Tando que após esse processo você vai poder restaurar o arquivo pacman.conf (Retirar as modificações ) oque vai permitir você usar mas de 1 Mirror !
Patrocínio
Destaques
Artigos
A Fundação da Confiança Digital: A Importância Estratégica de uma PKI CA na Segurança de Dados
Como enviar dicas ou artigos para o Viva o Linux
Como Ativar a Aceleração por GPU (ROCm) no Ollama para AMD Navi 10 (RX 5700 XT / 5600) no Gentoo
Dicas
Cairo Dock ainda funcional nos dias de hoje
Configuração de IP fixo via nmcli e resolução de nomes via /etc/hosts no Gentoo
Removendo o bloqueio por erros de senha no Gentoo (systemd)
Papel de Parede Animado no KDE Plasma 6 (Com dicas para Gentoo)
Homebrew: o gerenciador de pacotes que faltava para o Linux!
Tópicos
Tentando fazer um "linux ricing" mas falhando miseravelmente... (1)
Elilo e Sofrimento no Slackware (2)
Não consigo instalar as bibliotecas em Python pelo terminal. (1)
Top 10 do mês
-

Xerxes
1° lugar - 127.034 pts -

Fábio Berbert de Paula
2° lugar - 53.328 pts -

Buckminster
3° lugar - 30.078 pts -

Sidnei Serra
4° lugar - 22.750 pts -
Alberto Federman Neto.
5° lugar - 18.892 pts -

Mauricio Ferrari (LinuxProativo)
6° lugar - 18.416 pts -

Daniel Lara Souza
7° lugar - 18.258 pts -

Alessandro de Oliveira Faria (A.K.A. CABELO)
8° lugar - 17.209 pts -

edps
9° lugar - 16.029 pts -

Diego Mendes Rodrigues
10° lugar - 13.878 pts